Hitachi in Mass Production of High-Voltage and High-Output EV Inverter
Hitachi Automotive Systems, Ltd. announced the start of mass production for their 800-Volt compatible high voltage and high output electric vehicle (EV) inverter, which increases EV practicality and enables long-distance driving. The product contributes to both comfortable acceleration performance of the vehicle and faster charging times. For this inverter, the mounting technology of the power semiconductor was newly developed to realize an 800-Volt system.
Due to the product's high cooling performance and high voltage, compared to the previous generation of inverters, the new inverter delivers twice the voltage and 2.7-times higher power density.
Globally, the adoption of electric vehicles has been expanding in line with tightening environmental regulations. The European Union (EU) has made it mandatory to reduce average CO2 emissions from 120.5g/km in 2018 to below 95g/km by 2021. In China, automakers are also accelerating promotion of EVs, plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) and others, as they are required to comply with the New Energy Vehicle (NEV) credit policies that have been implemented starting 2019.
As most of today’s EVs are based on a 400-Volt system, in order to increase the vehicle's driving range, additional batteries with parallel connection are required. This results in increasing the battery capacity but also the charging time. However, an 800-Volt system enables the battery to be charged with the necessary amount of energy over a short period, allowing for fast charging of high capacity batteries.
To make the 800-Volt system possible, Hitachi Automotive Systems undertook a complete review of its inverter insulation structure to develop a compact power module with double-sided cooling and new high voltage insulation heat dissipation mounting technology. Compared to the previous generation of inverters, the solution delivers twice the voltage at 800 Volts and 94.3kVA/L, equating to 2.7 times higher power density.
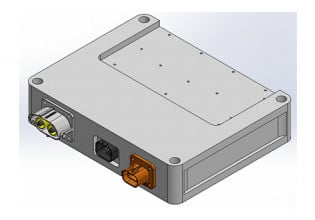
Double-sided Direct-cooling Power Module
 Double-sided Direct-cooling Power Module
Double-sided Direct-cooling Power Module
The thermal resistance of the power modules is improved at the expense of increasing the pressure loss in the cooling water channels. As this increases the resistance to water flow in the channels, the optimal point can be selected based on the cooling capacity. The power modules with double-sided direct cooling have approximately 35% better thermal resistance and providing a performance improvement of 30% or more in terms of current flow assuming use of power devices with the same chip size.
Improvements in the performance of modules with double-sided direct cooling mean less rise in junction temperature, and because the inverter is able to operate with the cooling water at a higher temperature.